Design and Specifications#
If you want to know how BeagleBone AI-64 is designed and the detailed specifications, then this chapter is for you. We are going to attept to provide you a short and crisp overview followed by discussing each hardware design element in detail.
Block Diagram and Overview#
BeagleBone AI-64 key components below shows the high level block diagram of BeagleBone AI-64 board surrounding TDA4VM SoC.
Fig. 78 BeagleBone AI-64 key components#
System on Chip (SoC)#
BeagleBone AI-64 uses TI J721E-family TDA4VM system-on-chip (SoC) which is part of the K3 Multicore SoC architecture platform and it is targeted for the reliability and low-latency needs of the automotive market provide for a great general purpose platform suitable for industrial automation, mobile robotics, building automation and numerous hobby projects.
The SoC designed as a low power, high performance and highly integrated device architecture, adding significant enhancement on processing power, graphics capability, video and imaging processing, virtualization and coherent memory support. In addition, these SoCs support state of the art security and functional safety features. For the remaining of this section device, SoC, and processor will be used interchangeably.
Fig. 79 System on Chip (SoC) block diagram#
Some of the main distinguished characteristics of the device are:
64-bit architecture with virtualization and coherent memory support, which leverages full processing capability of 64-bit Arm® Cortex®-A72
Fully programmable industrial communication subsystems to enable future-proof designs for customers that need to adopt the new Gigabit Time-sensitive Networks (TSN) standards, but still need full support on legacy protocols and continuous system optimization over the product deployment
Integration of vision hardware processing accelerators to facilitate extensive processing requirements in low power budget for automotive ADAS and machine vision applications
Integration of a general-purpose microcontroller unit (MCU) with a dual Arm® Cortex®-R5F MCU subsystem, available for general purpose use as two cores or in lockstep, intended to help customers achieve functional safety goals for their end products
Integration of a next-generation fixed and floating-point C71x Digital Signal Processor (DSP) that significantly boosts power over a broad range of general signal processing tasks for both general applications and automotive functions which also incorporates advanced techniques to improve control code efficiency and ease of programming such as branch prediction, protected pipeline, precise exception and virtual memory management
Tightly coupled Matrix Multiplication Accelerator (MMA) that extends the C71x DSP architecture’s scalar and vector facilities enabling deep learning and enhance vision, analytics and wide range of general applications. The achieved total TOPS (Tera Operations Per Second) performance significantly differentiates the device for single board computer in machine vision and deep learning applications
Key display features including flexibility to interface with different panel types (eDP, DSI, DPI) with multi-layer hardware composition
Integration of hardware features that help applications to achieve functional safety mechanisms
Robust security architecture with sandboxed DMSC controller managing all secure configurations with high performance client-server messaging scheme between secure DMSC and all cores
Simplified solution for power supply management, enabling lower cost system solution (on-die bias LDOs and power good comparators for minimal power sequencing requirements consistent with low cost supply design)
The device is composed of the following main subsystems, across different domains of the SoC, among others:
One dual-core 64-bit Arm Cortex-A72 microprocessor subsystem at up to 2.0 GHz and up to 24K DMIPS (Dhrystone Million Instructions per Second)
Up to three Microcontroller Units (MCU), based on dual-core Arm Cortex-R5F processor running at up to 1.0 GHz, up to 12K DMIPS
Up to two TMS320C66x DSP CorePac modules running at up to 1.35 GHz, up to 40 GFLOPS
One C71x floating point, vector DSP running at up to 1.0 GHz, up to 80 GFLOPS
One deep-learning MMA, up to 8 TOPS (8b) at 1.0 GHz
Up to two gigabit dual-core Programmable Real-Time Unit and Industrial Communication Subsystems (PRU_ICSSG)
Two Navigator Subsystems (NAVSS) for data movement and control
One multi-pipeline Display Subsystem (DSS) with one MIPI® Display Serial Interface Controller (DSI) and shared MIPI D-PHY Transmitter (DPHY_TX), one Embedded DisplayPort Transmitter (EDP) with shared Serializer/Deserializer (SERDES), and two MIPI Display Pixel Interface (DPI) ports
Two Camera Streaming Interface Receivers (CSI_RX_IF) with dedicated MIPI D-PHYs (DPHY_RX)
One Camera Streaming Interface Transmitter (CSI_TX_IF) with MIPI D-PHY Transmitter (DPHY_TX) shared with DSI
One Vision Processing Accelerator (VPAC) with image signal processor
One Depth and Motion Processing Accelerator (DMPAC)
One dual-core multi-standard HD Video Decoder (DECODER)
One dual-core multi-standard HD Video Encoder (ENCODER)
One Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
One Device Management and Security Controller (DMSC)
The device provides a rich set of peripherals such as:
- General connectivity peripherals, including:
Two 12-bit general purpose Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADC)
Ten Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) interfaces
Three Improved Inter-Integrated Circuit (I3C) controllers
Eleven master/slave Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interfaces (MCSPI)
Twelve configurable Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) interfaces
Ten General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) modules
- High-speed interfaces, including:
Two Gigabit Ethernet Switch (CPSW) modules
Two Dual-Role-Device (DRD) Universal Serial Bus Subsystems (USBSS) with integrated PHY
Four Peripheral Component Interconnect express (PCIe) Gen3 subsystems
- Flash memory interfaces, including:
One Octal SPI (OSPI) interface and one Quad SPI (QSPI) or one QSPI and one HyperBus^TM^
One General Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC) with Error Location Module (ELM) and 8- or 16-bit-wide data bus width (supports parallel NOR or NAND FLASH devices)
Three Multimedia Card/Secure Digital (MMCSD) controllers
One Universal Flash Storage (UFS) interface
- Industrial and control interfaces, including:
Sixteen Controller Area Network (MCAN) interfaces with flexible data rate support
Three Enhanced Capture (ECAP) modules
Six Enhanced Pulse-Width Modulation (EPWM) subsystems
Three Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (EQEP) modules
- Audio peripherals, including:
One Audio Tracking Logic (ATL)
Twelve Multichannel Audio Serial Port (MCASP) modules supporting up to 16 channels with independent TX/RX clock/sync domain
One Video Processing Front End (VPFE) interface module
The device also integrates:
Power distribution, reset controls and clock management components
- Power-management techniques for device power consumption minimization:
Adaptive Voltage Scaling (AVS)
Dynamic Frequency Scaling (DFS)
Gated clocks
Multiple voltage domains
Independently controlled power domains for major modules
Voltage and Temperature Management (VTM) module
Power-on Reset Generators (PRG)
Power Sleep Controllers (PSC)
Optimized interconnect (CBASS) architecture to enable latency-critical real time network and IO applications
- Control modules (CTRL_MMRs) mainly associated with device top-level configurations such as:
IO Pad and pin multiplexing configuration
PLL control and associated High-Speed Dividers (HSDIV)
Clock selection
Analog function controls
Multicore Shared Memory Controller (MSMC)
DDR Subsystem (DDRSS) with Error Correcting Code (ECC), supporting LPDDR4
1KB RAM with ECC support for C71x boot vectors
2KB RAM with ECC support for A72 and R5F boot vectors
512KB On-Chip SRAM protected by ECC
One Global Time Counter (GTC) module
Thirty 32-bit counter timers with compare and capture modes
Debug and trace capabilities
The device includes different modules for functional safety requirements support:
MCU island with dual lock step Arm Cortex-R5F
Safety enabled interconnect with implemented features to help with Freedom From Interference (FFI)
Twelve Real Time Interrupt (RTI) modules with Windowed Watchdog Timer (WWDT) functionality to monitor processor cores
Sixteen Dual-Clock Comparators (DCC) to monitor clocking sources during run-time
Three Error Signaling Modules (ESM) to enable error monitoring
Temperature monitoring sensors
ECC on all critical memories
Dedicated hardware Memory Cyclic Redundancy Check (MCRC) blocks
The device supports the following main security functionalities among others:
Secure Boot Management
Public Key Accelerator (PKA) for large vector math operation
Cryptographic acceleration (AES, 3DES, MD5, SHA1, SHA2-224, 256, 512 operation)
Trusted Execution Environment (TEE)
Secure storage support
On-the-fly encryption and authentication support for OSPI interface
The device is partitioned into three functional domains as shown in System on Chip (SoC) block diagram, each containing specific processing cores and peripherals:
Wake-up (WKUP) domain
Microcontroller (MCU) domain with one of the dual Cortex-R5 cluster
MAIN domain
Boot Modes#
There are two boot modes:
eMMC Boot: This is the default boot mode and will allow for the fastest boot time and will enable the board to boot out of the box using the pre-flashed OS image without having to purchase an microSD card or an microSD card writer.
SD Boot: This mode will boot from the microSD slot. This mode can be used to override what is on the eMMC device and can be used to program the eMMC when used in the manufacturing process or for field updates.
Important
This section needs more work and references to greater detail. Other boot modes are possible. Software to support USB and serial boot modes is not provided by beagleboard.org. Please contact TI for support of this feature.
A switch is provided to allow switching between the modes.
Holding the boot switch down during a removal and reapplication of power without a microSD card inserted will force the boot source to be the USB port and if nothing is detected on the USB client port, it will go to the serial port for download.
Without holding the switch, the board will boot try to boot from the eMMC. If it is empty, then it will try booting from the microSD slot, followed by the serial port, and then the USB port.
If you hold the boot switch down during the removal and reapplication of power to the board, and you have a microSD card inserted with a bootable image, the board will boot from the microSD card.
Note
Pressing the RESET button on the board will NOT result in a change of the boot mode. You MUST remove power and reapply power to change the boot mode. The boot pins are sampled during power on reset from the PMIC to the processor.The reset button on the board is a warm reset only and will not force a boot mode change.
Fig. 80 Boot config#
Fig. 81 MCU Bootmode#
Fig. 82 SYS Bootmode#
Power Sources#
The board can be powered from three different sources:
5V > 3A power supply plugged into the barrel jack
5V > 3A capable device plugged into the USB Type-C connector
The cape header pins
The power supply is not provided with the board but can be easily obtained from numerous sources. A 5V > 3A supply is mandatory to have with the board, but if there is a cape plugged into the board or you have a power hungry device or hub plugged into the host port, then more current may needed from the DC supply.
Power Management#
BeagleBone AI-64 power management invludes a lot of ICs from Texas Instruments,
DC/DC converter: TPS62813 and LM5141
LDO: TPS74801
PMICs: TPS65941213 and TPS65941111
Power Mux: TPS2121
Power Switch: TPS22965
1V1 DC/DC#
TPS62813 is a 3-A synchronous step-down DC/DC converter with high efficiency and ease of use. The TPS62813 family is based on a peak current mode control topology. The TPS62813 is designed for automotive applications such as infotainment and advanced driver assistance systems. Low resistive switches allow up to 4-A continuous output current at high ambient temperature. The switching frequency is externally adjustable from 1.8 MHz to 4 MHz and can also be synchronized to an external clock in the same frequency range. In PWM/PFM mode, the TPS62813 automatically enter power save mode at light loads to maintain high efficiency across the whole load range. The TPS62813 provide 1% output voltage accuracy in PWM mode which helps design a power supply with high output voltage accuracy. The SS/TR pin allows setting the start-up time or forming tracking of the output voltage to an external source. This feature allows external sequencing of different supply rails and limiting the inrush current during start-up.
Fig. 83 1V1 @ 1A DDR power supply#
1V1 & 2V5 LDO#
TPS74801 is a 1.5-A low-VIN (0.8 V) adjustable low-dropout (LDO) voltage regulator with power good and enable. The TPS748 low-dropout (LDO) linear regulator provides an easy-to-use robust power management solution for a wide variety of applications. User- programmable soft-start minimizes stress on the input power source by reducing capacitive inrush current on start-up. The soft-start is monotonic and designed for powering many different types of processors and ASICs. The enable input and power-good output allow easy sequencing with external regulators. This complete flexibility allows a solution to be configured that meets the sequencing requirements of FPGAs, DSPs, and other applications with special start-up requirements.
Fig. 84 1V1 USB3 & Ethernet power supply#
Fig. 85 2V5 Ethernet power supply#
3V3 DC/DC#
The LM5141 is a synchronous buck controller, intended for high voltage wide VIN step-down converter applications. The control method is peak current mode control. Current mode control provides inherent line feed-forward, cycle-by-cycle current limiting, and ease of loop compensation. The LM5141 features slew rate control to simplify the compliance with EMI requirements. The LM5141 has two selectable switching frequencies: 2.2 MHz and 440 kHz. Gate Drivers with Slew Rate Control that can be adjusted to reduce EMI. In light or no-load conditions, the LM5141 operates in skip cycle mode for improved low power efficiency. The LM5141 has a high voltage bias regulator with automatic switch-over to an external bias to reduce the IQ current from VIN. Additional features include frequency synchronization, cycle-by-cycle current limit, hiccup mode fault protection for sustained overload, and power good output.
Fig. 86 3V3 power supply#
PMIC#
TPS6594-Q1 is a Power Management IC (PMIC) with 5 BUCKs and 4 LDOs for Safety-Relevant Automotive Applications. The TPS6594-Q1 device provides four flexible multi-phase configurable BUCK regulators with 3.5 A output current per phase, and one additional BUCK regulator with 2 A output current. We are using two TPS6594-Q1 ICs TPS65941213 and TPS65941111 as PMIC-A and PMIC-B respectively as shown in AI-64 schematic snippets below.
TPS65941213 (PMIC-A)#
Fig. 87 PMIC A#
TPS65941111 (PMIC-B)#
Fig. 88 PMIC B#
Power mux#
TPS2121 is a 2.7-V to 22-V, 56-mΩ, 4.5-A, power mux with seamless switchover. The TPS212x devices are Dual-Input, Single-Output (DISO) Power Multiplexer (MUX) that are well suited for a variety of systems having multiple power sources. The devices will Automatically Detect, Select, and Seamlessly Transition between available inputs. Priority can be automatically given to the highest input voltage or manually assigned to a lower voltage input to support both ORing and Source Selection operations. A priority voltage supervisor is used to select an input source. An Ideal Diode operation is used to seamlessly transition between input sources. During switchover, the voltage drop is controlled to block reverse current before it happens and provide uninterrupted power to the load with minimal hold-up capacitance. Current limiting is used during startup and switchover to protect against overcurrent events, and also protects the device during normal operation. The output current limit can be adjusted with a single external resistor.
Fig. 89 Power mux#
Load switch#
TPS22965 is a 5.7-V, 6-A, 16-mΩ load switch with adj. rise time and optional output discharge. The TPS22965 is a single channel load switch that provides configurable rise time to minimize inrush current. The device contains an N-channel MOSFET that can operate over an input voltage range of 0.8 V to 5.7 V and can support a maximum continuous current of 6 A. The switch is controlled by an on and off input (ON), which is capable of interfacing directly with low-voltage control signals. In the TPS22965, a 225-Ω on-chip load resistor is added for quick output discharge when switch is turned off
Fig. 90 3V3 load switch#
General connectivity and expansion#
USB type C#
Fig. 91 USB type c#
Fig. 92 USB type c CC logic#
Fig. 93 USB type c signals#
USB3 Host Ports#
On the board is a stacked dual USB 3.0 Type A female connector with full LS/FS/HS/SS host support. The ports can provide power on/off control and up to 1.5A of current at 5V. Under USB power, the board will not be able to supply the full 1.5A.
Fig. 94 Dual USB3 ports#
Fig. 95 USB3 hub#
Fig. 96 USB3 hub over-current protection#
Cape headers#
P8 cape header#
Fig. 97 P8 cape header#
P9 cape header#
Fig. 98 P9 cape header#
Double pins (shorted)#
Fig. 99 P8 & P9 cape header pins that uses two pins of SoC#
Fan header#
Fig. 100 Fan header#
MicroSD Connector#
The board is equipped with a single microSD connector to act as the secondary boot source for the board and, if selected as such, can be the primary boot source. The connector will support larger capacity microSD cards. The microSD card is not provided with the board. Booting from MMC0 will be used to flash the eMMC in the production environment or can be used by the user to update the SW as needed.
Fig. 101 MicroSD card slot#
MikroBus port#
Fig. 102 MikroBus port#
PCIe Key E#
Fig. 103 PCIE Key E connector#
Fig. 104 PCIE Key E voltage translator (4ch)#
Fig. 105 PCIE Key E voltage translator (8ch)#
Gigabit Ethernet#
Fig. 109 Gigabit ethernet#
Fig. 110 Gigabit ethernet connector#
Memory, Media, and storage#
Described in the following sections are the three memory devices found on the board.
16GB Embedded MMC#
A single 16GB embedded MMC (eMMC) device is on the board. The device connects to the MMC1 port of the processor, allowing for 8bit wide access. Default boot mode for the board will be MMC1 with an option to change it to MMC0, the SD card slot, for booting from the SD card as a result of removing and reapplying the power to the board. Simply pressing the reset button will not change the boot mode. MMC0 cannot be used in 8Bit mode because the lower data pins are located on the pins used by the Ethernet port. This does not interfere with SD card operation but it does make it unsuitable for use as an eMMC port if the 8 bit feature is needed.
Fig. 111 16GB eMMC storage#
4GB LPDDR4#
A single (1024M x 16bits x 2channels) LPDDR4 4Gb memory device is used. The memory used is:
Kingston Q3222PM1WDGTK-U
Fig. 112 4GB LPDDR4 RAM#
4Kb EEPROM#
A single 4Kb EEPROM (24FC04HT-I/OT) is provided on I2C0 that holds the board information. This information includes board name, serial number, and revision information.
Fig. 113 Board ID EEPROM#
Multimedia I/O#
Fig. 114 CSI0 MIPI camera0 input#
Fig. 115 CSI1 MIPI camera1 input#
Fig. 116 DSI MIPI display output#
Fig. 117 Mini display port output#
Debug Ports#
Serial debug ports#
Two serial debug ports are provided on board via 3pin micro headers,
WKUP_UART0: Wake-up domain serial port
UART0: Main domain serial port
Note
In order to use the interfaces a 3pin micro to 6pin dupont adaptor header is required with a 6 pin USB to TTL adapter. The header is compatible with the one provided by FTDI and can be purchased for about $12 to $20 from various sources. Signals supported are TX and RX. None of the handshake signals are supported.
Fig. 118 WKUP UART0 debug port#
Fig. 119 UART0 debug port#
TagConnect#
Fig. 120 TagConnect JTAG debug port#
Mechanical specifications#
Dimensions & Weight#
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
Size |
104 * 83* 37 mm |
Max heigh |
23 mm |
PCB Size |
102.5*80*2.0 mm |
PCB Layers |
14 layers |
PCB Thickness |
2.0 mm |
RoHS compliant |
Yes |
Gross Weight |
249g |
Net Weight |
193g |
Board Dimensions#
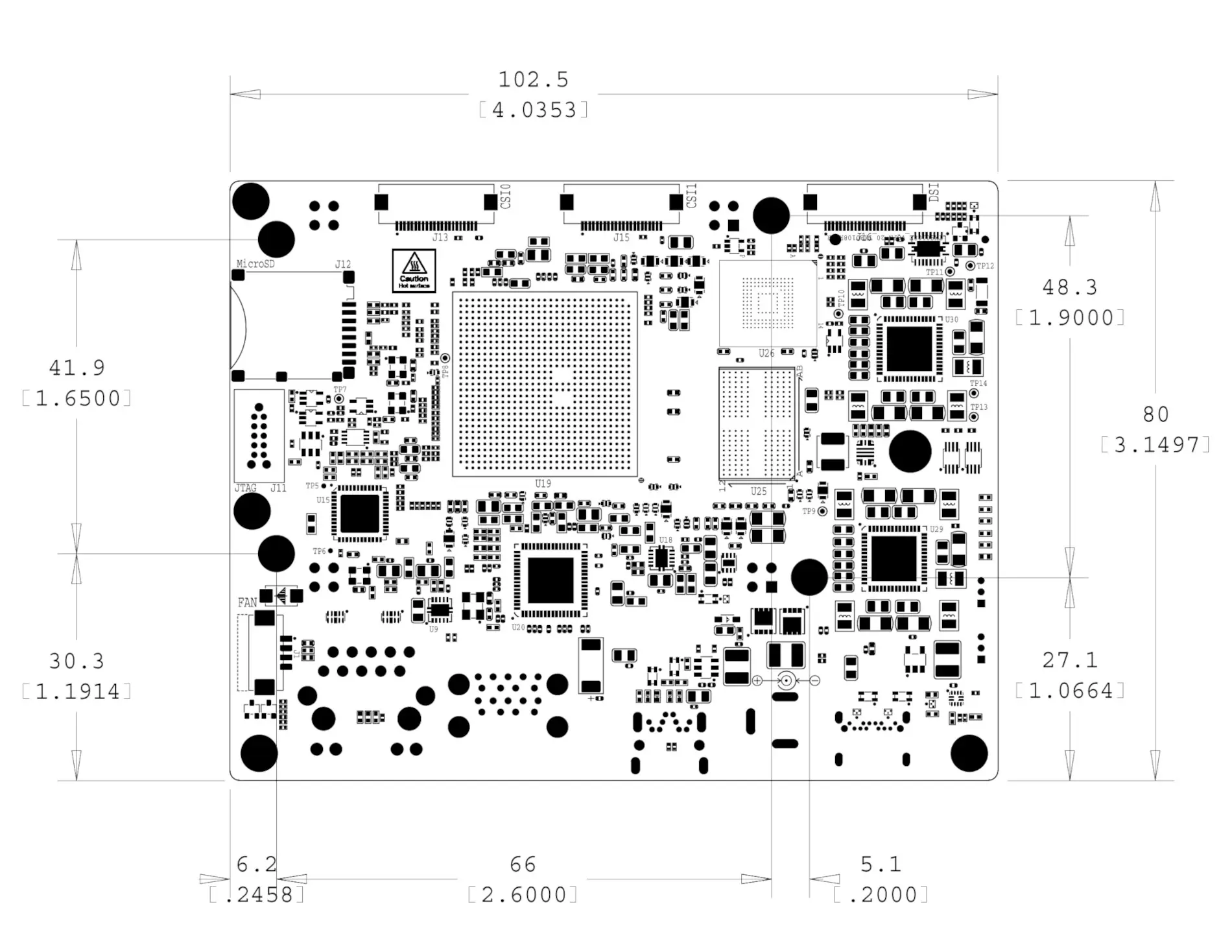
Fig. 121 BeagleBone AI-64 board dimensions#
PCB silkscreen#
Top silkscreen |
Bottom silkscreen |
|---|---|
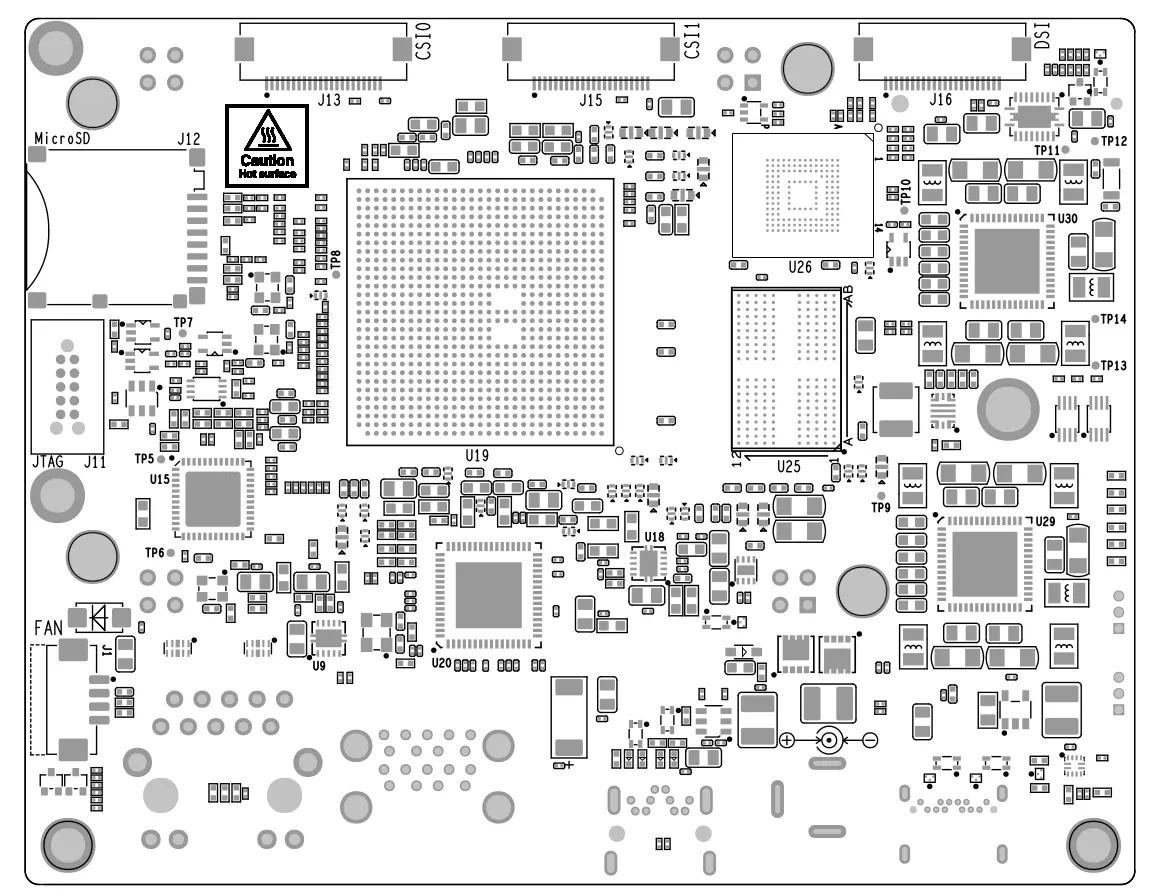
|
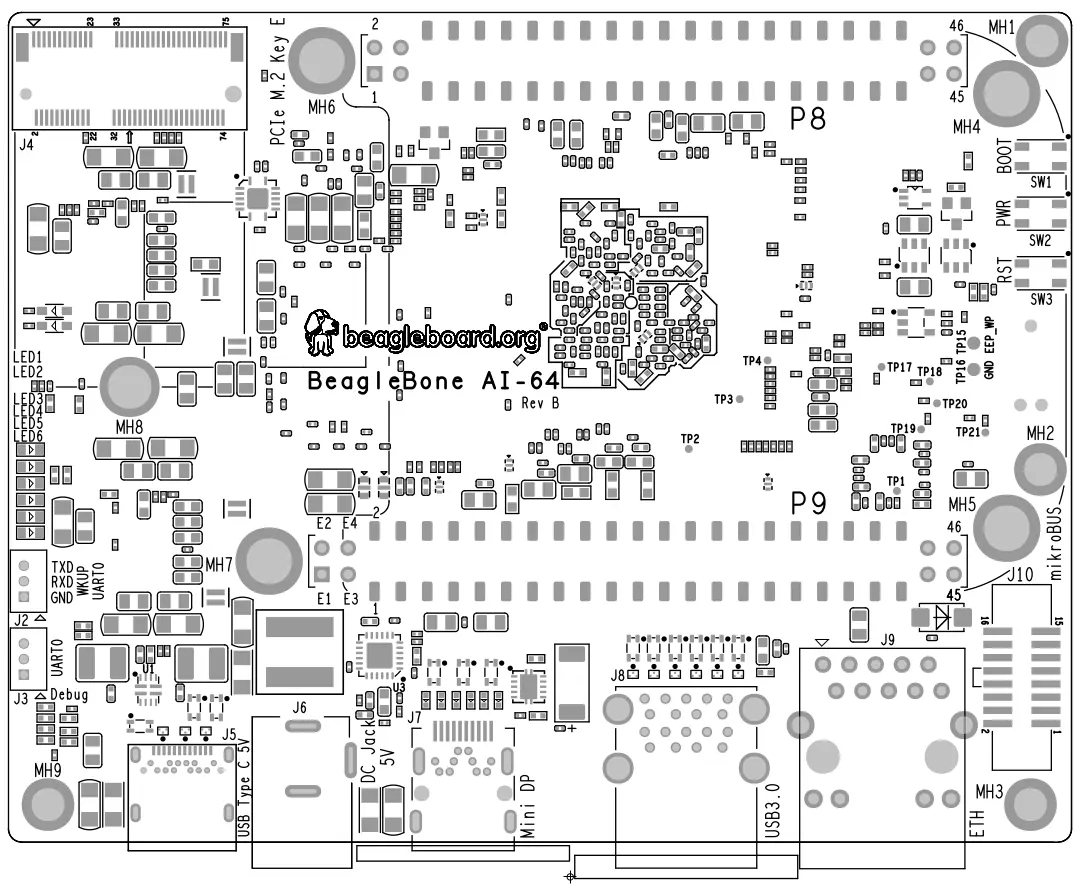
|
